Cloud Computing Defined
As its name implies, cloud computing delivers on-demand computing resources and services via the convenience of a virtual “cloud” that is accessible anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud computing allows users and organizations to remotely access servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics via the internet, eliminating the need for local infrastructure maintenance.
There are three primary models of cloud computing:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Users rent virtualized computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networks, from the service provider. Users have more control over the operating systems and applications running on the infrastructure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Users can deploy their applications onto the cloud infrastructure, leveraging the underlying computing resources provided by the service provider. The provider manages the infrastructure, and users focus on developing and running their applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Users access and use software applications hosted on the cloud infrastructure. The provider manages the entire infrastructure, including the applications, and users only need to access them through web browsers or specialized clients.
Investments in Innovation
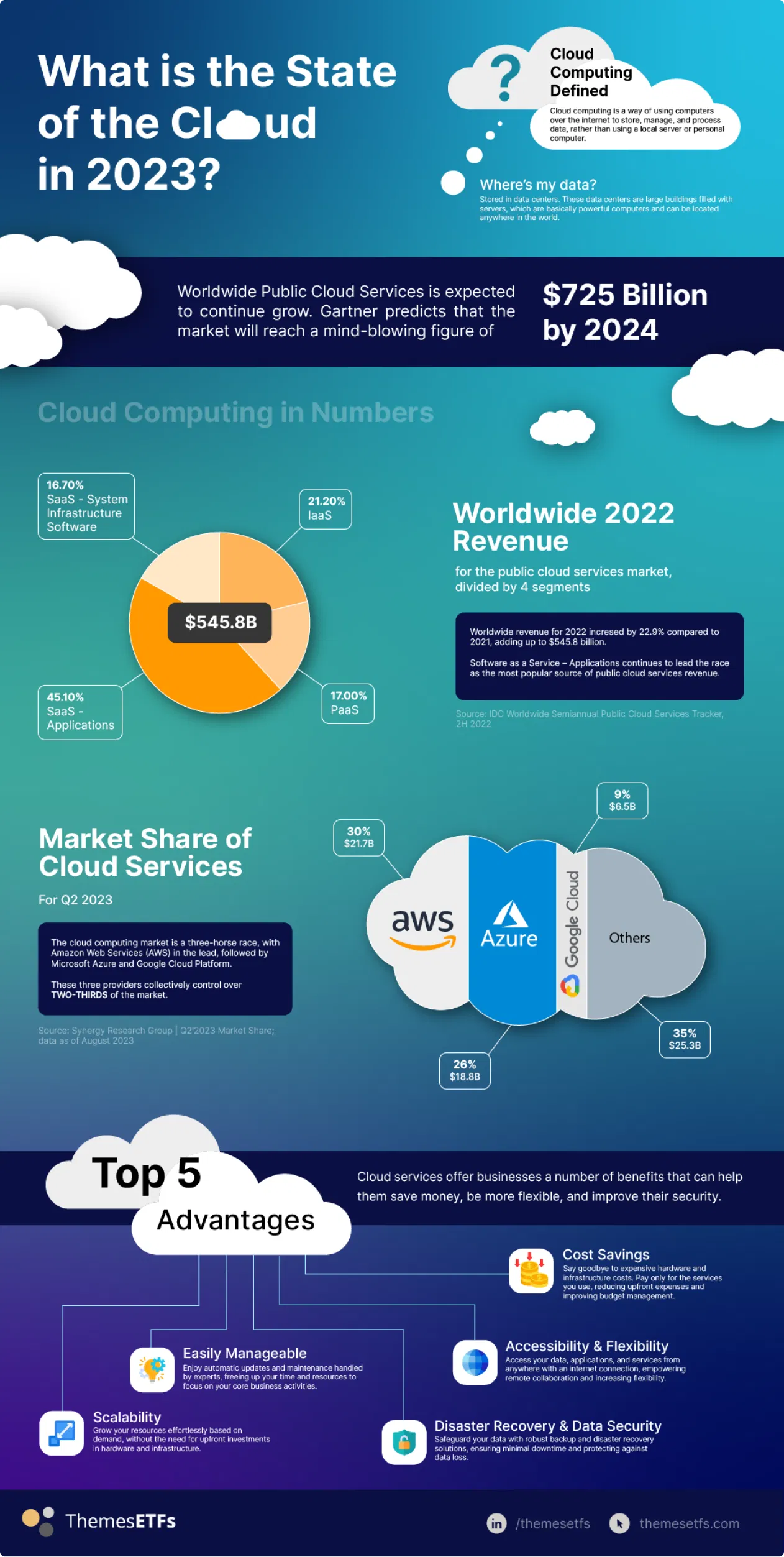
Given its extensive capabilities and convenience, the cloud computing industry continues to grow at a significant pace. According to economic estimates and consultancy forecasts:
The adoption of cloud computing technologies by global companies is expected to drive as much as $3 trillion in EBITDA value by 2030.1
Worldwide spending on cloud services is expected to grow 21.3% and top $724.56 billion by 2024.2
Cloud computing is expected to unlock $750 billion in innovation and $340 billion in cost reductions amongst the largest global firms by 2030.3
1Source: McKinsey & Company as of 31 December 2023
2Source: Gartner as of 31 December 2023
3Source: McKinsey & Company as of 31 December 2023
Service Segmentation
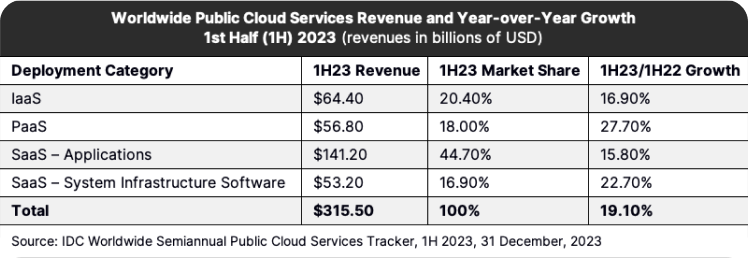
Amongst cloud computing services, Software as a Service (SaaS) Applications remain the largest segment, encompassing 44.7% of the overall industry market share.
However, Platform as a Service (PaaS) is the fastest expanding segment of the market, growing at 27.7% over the first half of 2023 relative to 2022, driven in part by increased demand for artificial intelligence applications.
Specific segments of cloud computing services remain driven by the demand of companies to adopt cutting-edge technologies and real-time analytics as a means to improve organizational efficiency and value creation.
Our Cloud Computing ETF (CLOD) seeks to track the Solactive Cloud Computing Index (SOLCLOUN), which identifies the largest 50 companies by market capitalization that derive their revenues from:
Digital Security
E-Commerce Infrastructure
Data Infrastructure
Data Architecture
Internet Infrastructure
Data Support
CLOD seeks to provide investment results that correspond generally to the price and yield performance, before fees and expenses, of the SOLCLOUN Index.